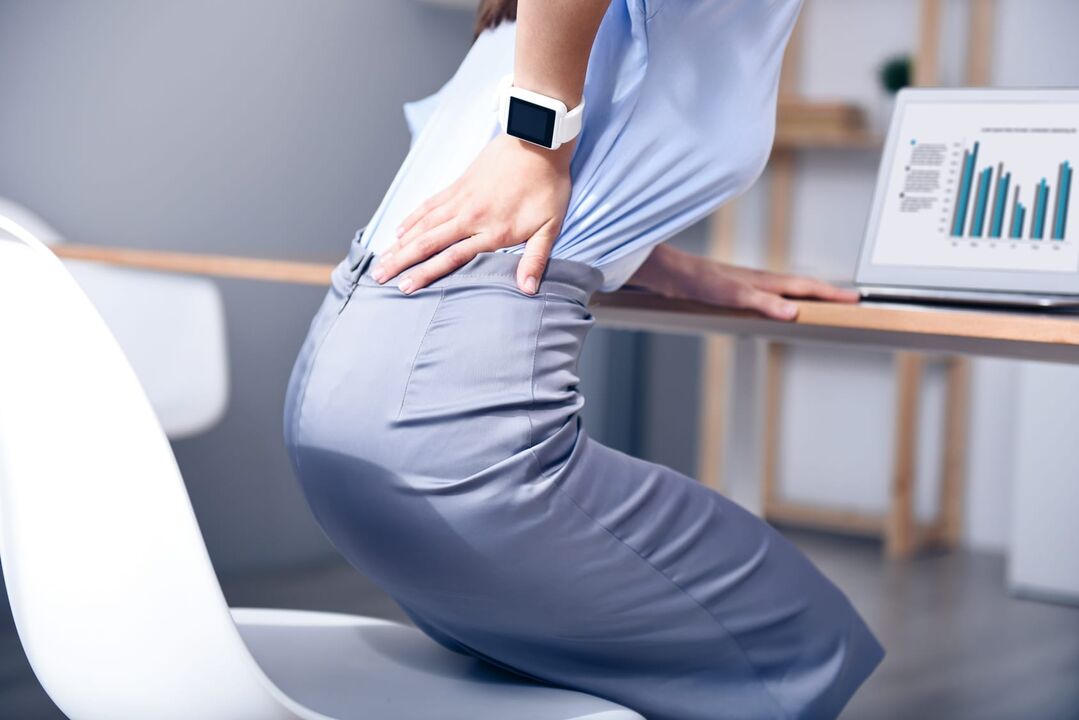
Lumbar osteoarthritis is a deformity of the spine in the lumbar region. The disease affects the discs, cartilage, spinal roots, and nerve fibers and causes back pain.
The CMRT clinic has been specialized in the conservative treatment of lumbar cartilage degeneration for more than 10 years. The centers are equipped with modern specialized equipment for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment and rehabilitation. Experienced specialists apply an individual approach, creating a wide range of treatments aimed at combating the pathology at all stages.

Importance!
Make an accurate diagnosis, determine the cause and nature of the disease, and only a qualified doctor at the internal appointment can prescribe an effective treatment.
reason
The main cause of the disease is the incorrect distribution of loads on the musculoskeletal system. This often happens when wearing high heels, carrying a bag sideways, with an uncomfortable position in a dream, or sedentary work. The elderly, pregnant women, newborns, professional athletes and office workers are at risk.
Other causes of lumbar osteoarthritis:
- injuries, bruises, broken arms, legs, spine
- damage to the organs of the musculoskeletal system
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, causing nutrient deficiencies
- body tension during prolonged exercise
- psychological disorder
- disorders of blood flow in the spine
- musculoskeletal system inflammation
- infection of internal organs and vertebrae
- joint stiffness, disc deviation
- protrusion and herniated disc
- severe poisoning
- metabolic disorder
- curvature of the pose
- sedentary lifestyle
- dehydration
- unbalanced diet
- lack of calcium and oxygen
- overweight
- bad habits
- age-related changes
- arthropathy
Symptoms of Lumbar Osteoarthritis
The intensity and nature of symptoms depend on the stage of the disease. The earlier the patient detects the signs of cartilage degeneration in the lumbar region, the more effective the treatment will be.
General symptoms:
- severe pain in the lower back, which may radiate down the legs, internal organs of the abdomen and pelvis
- pain in the kidneys and sacrum
- fatigue and tension in the lower back and spine
- Difficulty moving, walking, leaning and turning
- sometimes back pain
- Fatigue fast after light load
- crunches in the back, reduced mobility, pain at rest
- numbness in limbs
- spasms and cramps in muscles
- dizzy
- weakness and loss of strength
- decreased muscle tone and sensitivity
In men and women, the manifestations of lumbar osteoarthritis can be different. Men can have problems with potency. Women are more likely to experience pain in the pelvic area. When the deformed spine cannot fully support the back, the uterus and appendages take additional load and sometimes deviate from their normal physiological position.
Level
Osteoarthritis classification of the lumbar spine includes several types of diseases. By type of pain syndrome, there are:
back pain. acute symptoms. Presented by severe low back pain and inability to move. Occurs when muscle spasms, trauma, compression of discs and nerve roots.
Back pain. It is characterized by prolonged pain caused by hernias, protrusions, spondylolisthesis, sprains and other disorders of the musculoskeletal system.
Sciatica body pain. Severe pain in the lower back that radiates to the pelvis. The pain radiates to the sciatic nerve, preventing normal bending and straightening of the body, and pain-free sitting and standing.
Lumbar disc degeneration and radiculopathy are also distinguished.
Lumbar disc degeneration is accompanied by loss of sensation and numbness not only in the painful back but also in the legs, buttocks, thighs, and lower abdomen. Sometimes the body temperature rises, weakness, urinary incontinence appear, the patient loses weight.
Radiculopathy is manifested by paralysis of the nerve roots and reduced mobility of a person. Signs - tingling or pain in the entire lower body, impaired reflexes, decreased muscle tone and joints of the extremities.
Developmental stages of lumbar osteoarthritis
Doctors monitor the dynamics of pathology in four stages:
Firstly. Symptoms are almost invisible - they are diagnosed by X-rays. The stage begins with pathological processes in the pulpal cavity of the overlying disc and small cracks in the annulus.
Monday. The height of the discs decreases, causing the vertebrae to become closer together. This causes slippage and displacement of the vertebrae, accompanied by pain with movement.
The third day. Characterized by stiffness, instability, body paralysis in the coccyx, lower back and sacrum. This can be explained by protruding vertebrae, protrusion, dislocation and degenerative joint disease in the spine.
Wednesday. The most difficult level. On it, the functions of the spine are disrupted and bone growth (osteoporosis) is formed. Tumors can compress nerves or damage the integrity of the vertebrae.
Consequences of lumbar osteoarthritis
- Accumulation of too much salt in the body
- development of hernias, protrusions, vertebrae and disc prolapse
- chronic sciatica
- paralysis and paralysis of the legs
diagnose
Orthopedists, osteopaths, neurologists, rheumatologists, orthopedists, and surgeons can diagnose lumbar cartilage degeneration and other disorders of the musculoskeletal system. An accurate diagnosis can be made after:
- X-ray of the spine, which shows the condition of the bones, cartilage, and muscle tissue, as well as ligaments and tendons.
- Myelography is the study of cerebrospinal fluid using dye. With its help, the nerve roots of the spinal cord are studied and evaluated.
For a more detailed examination, doctors use CT and MRI. You can get a diagnosis in the CMRT network of clinics.
We also recommend undergoing plasma therapy, pharmacological procedures. To maintain health, chiropractic and chiropractic services, exercise therapy are recommended.
Treatment of lumbar osteoarthritis
A neurologist is engaged in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the lumbar spine. The standard treatment regimen looks like this: the doctor makes a diagnosis, determines the extent of the disease development, and identifies complications. With this in mind, he chooses a treatment - conservative or surgical.
physical therapy
Exercise therapy for osteoarthritis of the spine is carried out in a fully equipped room under the supervision of a physician. Classes are performed when remission occurs and the patient is pain-free. The doctor monitors the patient's condition during physical activity, if pain or discomfort occurs, the doctor will adjust the exercise or cancel it.
Each gymnastics lesson takes place in several stages. During the warm-up, the patient performs light exercises to warm up the muscles and disperse the blood. In the main part - exercises for the affected spine. Finally, relax muscles.
Physiotherapy for spondylolisthesis
Physical therapy procedures are performed to relieve pain, improve blood circulation and tissue nutrition, and reduce inflammation. Usually, patients are prescribed:
- electrophoresis, which helps to reduce the neurological manifestations of the disease
- dynamic therapy with the action of electric currents of different intensity, providing effective pain relief even in severe pain
- ultrasound therapy with exposure along the affected spine
- magnetotherapy with an alternating magnetic field
To achieve the best effect, the patient is prescribed several physiotherapeutic procedures.
Kinesiology recording
For anesthesia, a cotton pad with hot melt glue is used. There are special treatment applications for neck, chest, back and joint problems.
Injections for Lumbar Osteoarthritis
With lumbar osteoarthritis, your doctor may prescribe the following injections to treat:
- chondroprotectors protect cartilage tissue from further destruction, slowing the development of dystrophy
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce inflammation, have a fever-reducing and pain-relieving effect by reducing swelling in the inflamed area
- vitamin complex restores blood circulation in the affected areas, accelerates the renewal of nerve fibers, improves the condition of the whole body
Injections can be prescribed only by a doctor, since the treatment has contraindications. For example, many drugs are prohibited for allergy sufferers, pregnant and lactating mothers.
Drug treatment
Doctors try to stay away from this treatment, but in severe cases they prescribe the following drugs to treat lumbar osteoarthritis:
- pain relievers only have an additional analgesic or anti-inflammatory effect
- antispasmodics reduce muscle spasms, so that pressure on nerve endings stops and pain subsides
- Vasodilators improve blood microcirculation, helping to reduce spine recovery time after osteoarthritis treatment
Treatment with tablets is carried out separately or in combination with injections. For example, a certain drug is prescribed as a tablet, and if it is not effective enough, it is prescribed as an injection.
Surgical intervention
The operation is a radical measure, it is used only in severe cases. During surgery, the doctor completely removes the cause of pain and stabilizes the spine.
Prevention of Lumbar Osteoarthritis
- Make a moderate schedule of sports and exercise therapy
- take a break at work every hour for 5-7 minutes
- sleep on a flat surface or buy an orthopedic mattress
- wear comfortable shoes that fit
Which doctor to contact?
The neurologist makes the correct diagnosis, prescribes treatment, and corrects it if needed. If the disease is accompanied by severe pain or dysfunction of internal organs, it may be necessary to consult other specialists.
frequently asked Questions
How to provide support in acute pain in lumbar osteoarthritis?
A patient with back pain should be helped to lie down in a comfortable position to relieve the pain. Then you should consult your doctor.
Is it possible to exercise with lumbar osteoarthritis?
In the acute phase, physical exercises are contraindicated, the patient must adhere to bed rest. When the pain disappears, the patient should exercise therapy - perform general strengthening exercises. They must be selected by a doctor. At the same time, it is important to monitor your health during physical activity. If any exercise causes pain, it is important to limit the intensity or eliminate it.